In the modern world that is so steeped in technology and is so dominated by the digital reality of the Internet and the World Wide Web, every app we download and use, every page we visit on the Internet, and every ‘smart’ device we own and employ is comprised of two basic elements: hardware and software. Hardware and software are frequently mentioned together, but they are actually two strictly different things that cannot be accomplished alone.
A computer system consists of two main parts: Hardware and Software. Hardware refers to the physical components, like the CPU and RAM, while Software includes the programs and applications that control these components. Both are essential for the computer to function properly, and they work together to ensure smooth performance. This article will highlight their key differences and how they interact in modern computing.
What Is Hardware?
Hardware means the tangible parts of a computer and other electronic device that one can see and touch. Hardware builds the base for any computer device.Computer hardware refers to the physical components of a computer that you can touch and see. These parts work together to process data and perform tasks. Examples include the Processor, Memory Devices, Monitor, Printer, Keyboard, Mouse, and Central Processing Unit (CPU).
Internal hardware
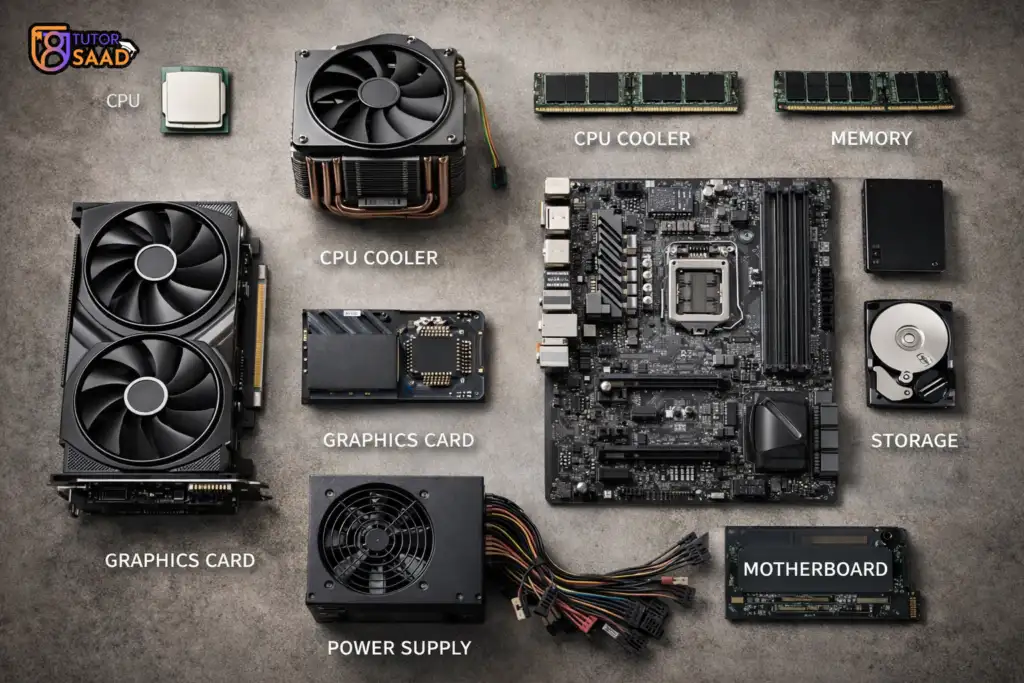
Internal hardware refers to the essential physical components located inside a computer’s case that work together to process data and run software, including the CPU (brain), RAM (short-term memory), Motherboard (connector), Storage (SSD/HDD for long-term data), GPU (graphics), Power Supply, and Cooling Fans, all crucial for the computer’s core functions.
Key Internal Hardware Components
- Central Processing Unit (CPU): Executes instructions and performs calculations, often called the computer’s brain.
- Motherboard: The main circuit board that connects and allows communication between all other components.
- Random Access Memory (RAM): Fast, temporary storage for data and programs currently in use, cleared when the computer turns off.
- Storage (SSD/HDD): Solid State Drives (SSDs) or Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) for permanent storage of the OS, apps, and files.
- Graphics Processing Unit (GPU): Renders images and video for display, crucial for gaming and professional graphics.
- Power Supply Unit (PSU): Converts wall power (AC) to the lower voltage DC power needed by internal components.
- Cooling Systems (Fans/Heatsinks): Regulate temperature to prevent overheating, especially from the CPU and GPU.
- Sound Card & Network Interface Card (NIC): Handle audio output/input and network connectivity, often built into the motherboard.

Key Function
These parts work in concert: the CPU fetches instructions from RAM, processes them, sends data to the GPU for display, and stores long-term info on the drive, all facilitated by the motherboard and powered by the PSU, with fans keeping everything cool
External hardware
These are devices that are external to the computer case that are connected to the computer for input, output, storage, or communication. These are also known as “peripherals” such as keyboards, mice (input); monitors, printers (output); and external drives (storage), among others that expand the capabilities of the computer apart from its internal components such as the CPU or RAM.
Types and Examples
Input Devices: These devices transfer data to the computer. i.e Keyboard, Mouse, Trackpad, Touchpad, Microphone, Webcam, Scanner.
Output Devices: These receive information from a computer. i.e Monitor, Printer, Speakers, Headphones ,Projector, Display Screen.
Storage Devices: This device stores the data externally. External Hard Drives (HDD/SSD), USB Flash ,External Optical Drives (CD/DVD).
Communication / Networking: Network router, external modem, external GPS modules with USB or Bluetooth connectivity.

Key Function
User Interaction: Enables a user to control the computer (input) and view or hear the output.
Functionality Upgrade: Adds functionality not provided by the original product, such as the ability to print or scan, or additional
Data Transfer: Facilitates data transfer between devices quickly.
Computer Software
Software – a set of instructions or programs that tells a computer what to do or how to perform a specific task (computer software runs on hardware).Software is a collection of instructions, procedures, and documentation that performs different tasks on a computer system. We can say also Computer Software is a programming code executed on a computer processor. The code can be machine-level code or code written for an operating system.
Examples of software are MS- Word, Excel, PowerPoint, Google Chrome, Photoshop, MySQL, etc.
Main types of software
- Systems Software
- Application software
Application software
A computer program that provides users with tools to accomplish a specific task. Application software is a type of software designed to help users perform specific tasks or activities on a computer. It runs on top of system software and allows users to interact with the computer to accomplish tasks such as writing documents, browsing the internet, editing images, or managing data. Importance or Benefit: It makes computers useful for end users by enabling task-oriented work in education, business, communication, and entertainment.
Examples of application software: word processing, spreadsheets, presentation, database management, Internet browsers, email programs, media players, accounting, pronunciation, translation, desktop publishing, enterprise, etc.
System Software
It is designed to run a computer’s hardware and application software, and make the computer system available for use. It serves as the interface between hardware,
Main functions of system software allocating system resources, managing storage space, storing and retrieval of files, providing security, etc.
Main types of systems software (operating system, device driver, utility software, programming software, etc)
Operating system (OS) – a software that controls and coordinates the computer hardware devices and runs other software and applications on a computer. It is the main part of system software and a computer will not function without it.

- Main functions of an operating system – booting the computer, managing system resources (CPU, memory, storage devices, printer, etc.), managing files, handling input and output, executing and providing services for application software, etc.
- Examples of operating system: Microsoft Windows, Apple iOS, Android OS, macOS, Linux, etc.
Device driver – a software program that is designed to control a particular hardware device that is attached to a computer.
- The main purpose of device driver – it acts as a translator between the hardware device and operating systems or applications that use it.
- It instructs computer on how to communicate with the device by translating the operating system’s instructions into a language that a device can understand in order to perform the necessary task.
- Examples of device driver: printer driver, display driver, USB driver, sound card driver, motherboard driver, ROM driver, etc.
Utility software – a type of system software that helps set up, analyze, configure, strengthen, maintain a computer and performs a very specific task (e.g. antivirus software, backup software, memory tester, screen saver, etc.)
Software Licensing
A software license informs the user of the ways that the software can and cannot be used, including whether there will be a cost involved.
Freeware
Software that is free to use. No payment required. Usually cannot be modified
Examples: Google Chrome ,VLC Media Player ,Skype
Key Point: Free to use, but the owner keeps the rights.
Shareware
Software given free for a limited time or with limited features Payment required to unlock full version Used for testing before buying
Examples: WinRAR Trial versions of antivirus software
Key Point: Try before you buy.
Paid Software (Commercial software)
Requires a purchase to use .Mostly a one-time payment. Full features are only available after purchase
Examples: One-time software licenses – Microsoft Office Adobe Photoshop (earlier versions) AutoCAD
Key Point: Use once, pay once (use for the version).
Subscription-Based Software
Payment is done on a monthly The software is only active during the subscription period.
Updates were continuous
Examples: Microsoft 365, Adobe Creative Cloud, Adobe Color, Netflix (software & service)
Basics of Programming
To create applications that computers can run, programmers create computer programs by writing code using programming languages.
Some of the most popular programming languages include:
- Python – Easy to learn. Used in data science, artificial intelligence, and automation.
- Java – Can be run on any platform; commonly used for building large business applications and on the Android Operating System.
- C – A fast language that is widely used to create computer operating systems.
- C++ – An updated version of the C language; this version also uses advanced features like graphics and video games.
- JavaScript – JavaScript allows for the creation of dynamic web pages and web applications.
Execution Pathway of Program
- The code is written by programmers.
- The code is converted from a high-level language to a low-level machine language (Machine Code) by the Compiler.
- The program runs via an Interpreter; an Interpreter executes the process line-by-line.
- Examples of languages that use Compilers: C, C++.
- Examples of languages that use Interpreters: Python, JavaScript.
Computer Software Security
- What are Antivirus Products Used For? They will help to detect and remove malicious software and viruses. They are designed to protect against viruses, spyware and malware.
- What are the Dangers of Using Pirated Software? Pirated software is illegal and generally unsafe because it may contain hidden malware. Because they are illegal, they also do not come with the benefit of software updates/technical support.
- What Makes a Strong Password? A strong password has both upper case and lower case letters, numbers, symbols, NO personal information included, and you should use different passwords for each account.
- What are the Types of Malware? A Computer Virus is a program that attaches itself to a file or program and will cause damage to that file or program and spread itself to other computer systems. The term Malware is used as a general category for all programs that are designed for malicious purposes. Ransomware is a type of malware that is used to encrypt a user’s data, then requires the user to pay a ransom to be able to access their data.
Computer Software Security
Efficient code
Optimized algorithms run faster than inefficient algorithms. Better programs will consume less memory than poor ones. Optimized programs will have fewer bugs and crashes.
Hardware Resources
The quantity of RAM within your computer influences the number of applications you can run simultaneously. The speed of your CPU will determine how quickly you can process data. The number of Running Background Processes will influence how quickly your computer responds to commands.
Difference between Hardware and Software
| Basic Definition | Hardware is a physical part of the computer that causes the processing of data. | Software is a set of instructions that tells a computer exactly what to do. |
| Development | It is manufactured. | It is developed and engineered. |
| Dependency | Hardware cannot perform any task without software. | The software can not be executed without hardware. |
| Process of creating | Electronic and other materials are used to create hardware. | Created by utilizing a computer language to write instructions. |
| Tangible | Hardware is tangible as hardware is a physical electronic device, that can be touched. | Software is intangible as we can see and also use the software but can’t touch them. |
| Durability | Hardware typically wears out over time. | The software does not wear out with time. However, it may contain flaws and glitches. |
| Types | It has four main categories: Input Devices Output Devices Storage Devices Internal Components. | It is mainly divided into System software Application software. |
| Virus effect | Hardware is not affected by computer viruses. | Software is affected by computer viruses. |
| Transfer | It cannot be transferred from one place to another electrically through the network. | It can be transferred via a network means. |
| Machine-Level language | Only machine-level language is known to be understood by hardware. | The program accepts human-readable input, interprets it in machine-level language, and sends it to hardware for additional processing. |
| Replacement | If the hardware is damaged, it is replaced with a new one. | If the software is damaged, its backup copy can be reinstalled. |
| Failures | Dust, overheating, humidity, and other factors are commonly responsible for hardware failures. | Overloading, systematic error, major-minor version error, and other factors are commonly responsible for software failures. |
| Examples | Ex: Keyboard, Mouse, Monitor, Printer, CPU, Hard disk, RAM, ROM, etc. | Ex: MS Word, Excel, PowerPoint, Photoshop, MySQL, etc. |






